The working principle of the shredder is revealed: How to ensure information security?
1. The basic working principle of a shredder
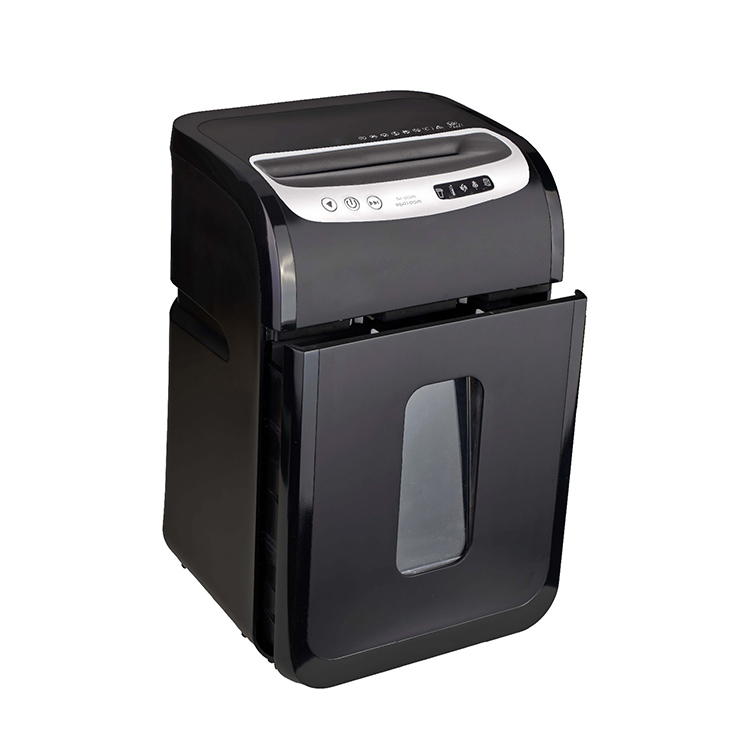
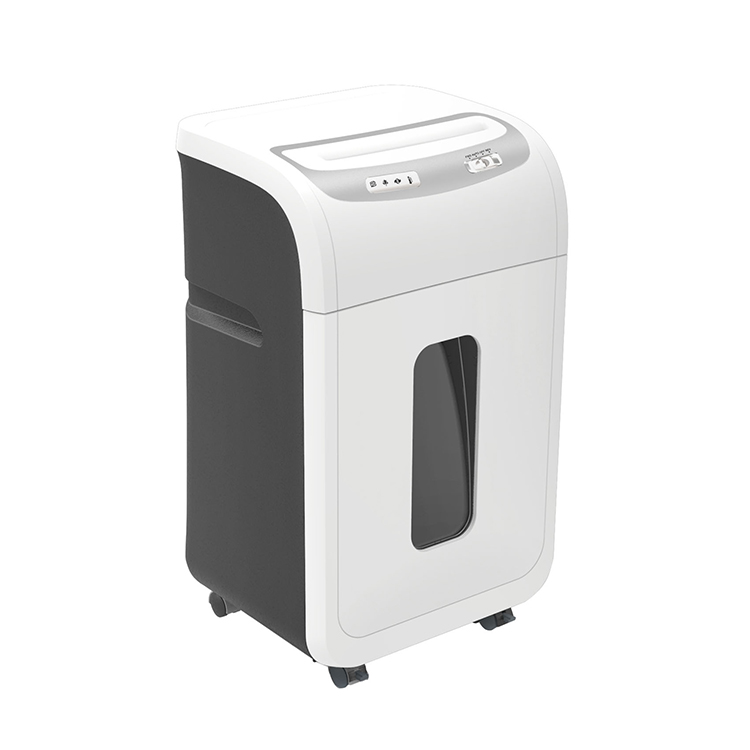
The core working mechanism of a Paper Shredder into small pieces or thin strips through a set of high-speed rotating blades, making the text or pattern on the paper unrecognizable. Different types of shredders use different cutting methods and are designed for different security needs:
Strip-Cut Shredder
This is the most basic and common type of shredder. The paper after cutting becomes a long strip with a width of about 6 mm. This cutting method can quickly process a large number of files with high efficiency and is suitable for general home or office use. However, due to the large fragments, there is a certain probability of restoring the file content by splicing in theory, so the security level is low.
Cross-Cut Shredder
The cross-cut shredder not only cuts the paper into strips longitudinally, but also cuts it into smaller rectangular fragments horizontally. The fragments after cutting are usually about 4x40 mm in size, which is smaller than strip cutting, making the restoration difficulty much higher. This type is suitable for general enterprises and occasions requiring medium security protection.
Micro-Cut Shredder
Micro-Cut technology can cut paper into extremely fine particles, with the size of the fragments being only a few millimeters square and the shape similar to debris. This type of shredder is generally used for the destruction of documents that require high security protection, such as bank bills, medical records, confidential contracts, etc., which can greatly reduce the risk of information recovery.
Particle-Cut Shredder
It is an upgraded version of micro-cutting. The particles cut are finer and irregular in shape, meeting the security standards of government or military confidential documents. This type of shredder is often larger in size and more expensive, and is mostly used in specialized information security agencies and large enterprises.
The blades of the shredder are usually made of high-hardness steel and can rotate continuously at high speed to ensure that the paper is cut evenly and thoroughly. Modern shredders are also equipped with gear transmission and motor protection systems to improve performance stability and service life. Some high-end models support automatic paper feeding. Just put a stack of paper in, and the machine will automatically feed the paper into the blade one by one, greatly improving office efficiency.
2. How does the shredder ensure information security?
As a physical information destruction tool, the shredder not only shreds paper, but is also a key safeguard to prevent information from being illegally obtained.
Prevent information recovery
After cutting paper into extremely small pieces, the originally clear text, numbers, patterns and other information become fragmented. In particular, the shredded paper scraps of particles and granules are extremely small and irregular in shape, and it is almost impossible to restore the original file through manual splicing or digital scanning. This effectively avoids the risk of thieves splicing information through waste paper recycling.
Reduce physical storage risks
Many sensitive information is still stored in paper form in filing cabinets and office folders. If these documents are not properly destroyed, they will cause information leakage once they are stolen or lost. The shredder can completely destroy paper information, making it impossible to use or abuse it a second time, reducing security risks from the source.
Comply with data protection regulations
In recent years, the laws and regulations on personal privacy and data protection have become increasingly stringent around the world, such as the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the US's Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which clearly require institutions to safely destroy paper materials containing personal sensitive information. Using a shredder not only meets legal compliance requirements, but also avoids huge fines and reputation losses caused by information leaks.
Double protection of environmental protection and safety
The shredded paper is not only safe, but also convenient for recycling and reuse, which is in line with modern environmental protection concepts. The design of many shredders also takes environmental factors into consideration, such as low energy consumption and low noise, so that users can reduce the negative impact on the environment while ensuring information security.
3. Best practices for using shredders
In order to maximize the safety benefits and service life of shredders, it is crucial to master the correct usage and maintenance techniques.
Choose the right type of shredder
Choose the right shredder according to the confidentiality level of the file. Strip or cross-cut shredders can be used for daily ordinary documents; micro-particle or granular shredders should be used for confidential documents. Enterprises should evaluate their own security needs to avoid "shooting small birds with big guns" or "blindly saving".
Regular maintenance
Long-term use of shredders can easily accumulate paper scraps, causing blade blunting or paper jams. It is recommended to clean the shredder box regularly, clean the residual paper scraps on the blade in time, and lubricate the blade regularly with special lubricating oil to maintain cutting efficiency and machine life.
Reasonable classification and processing
For documents containing information of different security levels, they should be destroyed in categories. Highly confidential documents should be shredded multiple times first, and ordinary documents can choose standard shredding. Avoid mixing non-confidential documents with confidential documents to improve shredding efficiency.
Combined with electronic destruction methods
Modern enterprise information exists in both paper and electronic forms. Shredding alone cannot solve the problem of electronic data security. It should be combined with electronic file security management, such as data encryption, regular hard disk cleaning and other measures to ensure all-round destruction of information.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch عربى
عربى
 0
0


















